Western Sydney University has an institutional Covidence license. Covidence is a web-based tool that will help you through the process of screening your references, data extraction, and keeping track of your work. It is useful for researchers conducting a systematic review, meta-analysis, or clinical guideline.
Join the Western Sydney University Covidence licence
The Library offers regular training in systematic searching and provides an overview of complex reviews.
Attend training for advice on systematic searching and complex reviews Learn more about Systematic and Complex Reviews
More about Covidence
In Covidence you can:
Import references
Covidence works seamlessly with your favorite reference managers like EndNote, Zotero, Refworks, Mendeley or any tool that support RIS, CSV or PubMed XML formats. Covidence can remove duplicates for you, however, as with any system, you will need to do a manual check.Screen title & abstract
Breeze through screening with keyword highlighting & a lightning quick interface. Covidence keeps full records of who voted and supports single or dual screeners.Bulk PDF import
Transfer PDFs stored in your reference manager to Covidence in a few clicks.Screen full text
Decide quickly on studies in full text. Capture reasons for exclusion and any notes so you can resolve any disagreements quickly, with a click of a button.Create forms
Be in control and stay focused on your PICO question. Customizable extraction forms means you only spend time extracting what you need.Customize risk of bias
Automatically populate your risk of bias tables by highlighting and commenting on text directly in your PDF.Conduct data extraction
Extract data efficiently with a side-by-side view of your customized form and PDF. Then, when you are done, easily compare your form with other reviewers.Export
Covidence exports to all the common formats so you can continue your review in your preferred software.Collaborate
You can invite other reviewers (including external colleagues) to work with you on the project.
For help using Covidence
Covidence offers monthly training webinars (registration required), along with 24-hour methodological or technical support at support@covidence.org.
Covidence Academy is also a great resource containing useful ‘How to’ guides, step-by-step videos on features, and helpful links to additional resources. Their Knowledge Base can help you with Getting Started with Covidence with your review, or you can refer to their online video tutorials for assistance.
Logged into your Covidence account and need help? Click the question mark in the upper right hand corner to access support.
Creating a review using the Western Sydney University unlimited licence
After clicking the link “Create new review”, you will have the option to use your personal account license or select the Western Sydney University account.
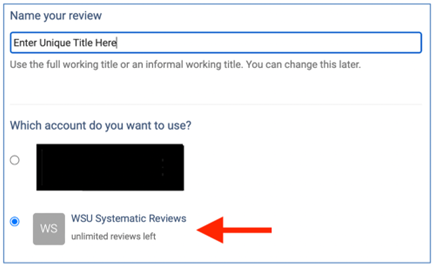 Reviews created under the institutional license will be visible to the administrators of the Western Sydney University Covidence account. Your personal account review(s) will only be seen by you.
Reviews created under the institutional license will be visible to the administrators of the Western Sydney University Covidence account. Your personal account review(s) will only be seen by you.
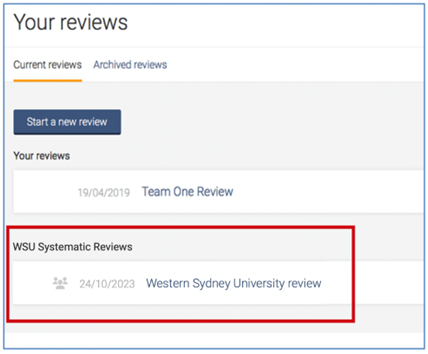
Once you have created a review or accepted an invitation to another Western Sydney University account review, the title will appear in a separate section on your account homepage:
Working with review team members from other institutions
Once a review is created, you can add co-reviewers.
- From the homepage (Your reviews), select the review you wish to add co-reviewers to and click on “Settings”
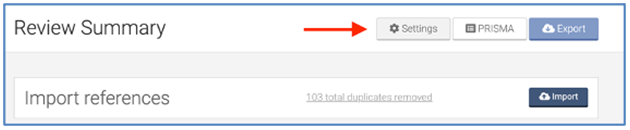
- From the review Settings, navigate to “Add/remove reviewers”
- Click on “Invite another reviewer”and enter your reviewer’s first name and email addresses to invite them